Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Without using truth table show that ∼ (p∨ q)∨ (∼ p∧ q)≡∼ p Join / Login > 11th > Applied Mathematics > Mathematical and logical reasoning > Mathematically accepted statementsSolution for Construct a truth table for the symbolic expressions Exercise 1∼p∨∼(q∧r) Exercise 2p∧r→(q∨∼r)Show that (P → Q)∨ (Q→ P) is a tautology I construct the truth table for (P → Q)∨ (Q→ P) and show that the formula is always true P Q P → Q Q→ P (P → Q)∨ (Q→ P)
Solved Use A Truth Table To Determine Whether The Argument Is Valid Or Invalid Course Hero
If p then q q therefore p truth table
If p then q q therefore p truth table-Using truth table prove that p ↔ q = (p ∧ q) ∨ (~p ∧ ~q) Maharashtra State Board HSC Science (Computer Science) 12th Board Exam Question Papers 181 Textbook Solutions Online Tests 60 Important Solutions 3532 Question Bank SolutionsExperts are tested by
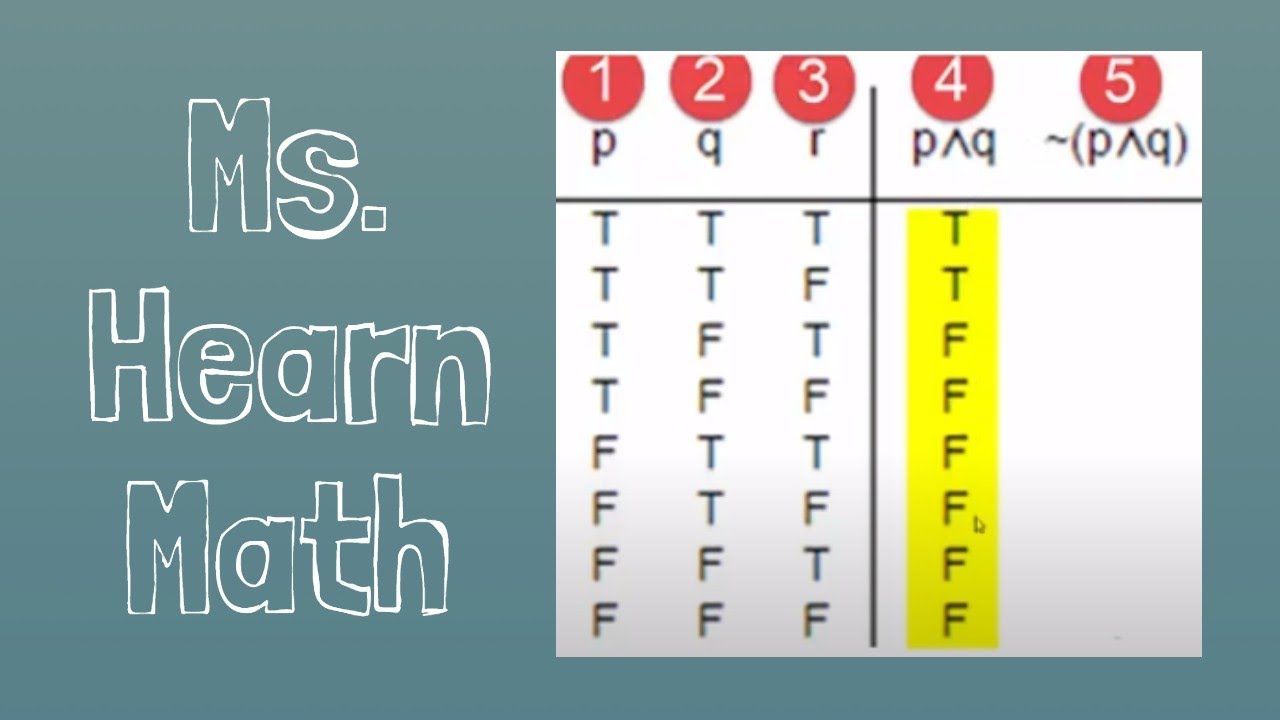



Logic Truth Table For P Q R Q Youtube
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedbackTautologies A proposition p is called a tautology if and only if vp = t holds for all valuations v on Prop In other words, p is a tautology if and only if in a truth table itSolve the following equations using truth tables and make an observation from all its truth values p ∧ (¬p ∨ q) → p p ∧ (q → r) → (q →r) (p ∨ q) ∧ (p → r) ∧ (q → r) → r (p ↔ q) ∨ (q ↔ r) ∨ (r ↔ p) Expert Answer Who are the experts?
Construct a truth table to decide if the two statements are equivalent~p ∧ ~q;Recall that P ∨ ¬ Q is the same as Q → P So the formula of the question is equivalent to ( Q → P) ∧ ( R → Q) ∧ ( P → R) Since implication is transitive (if A → B and B → C then A → C follows) this formula implies that P → Q (since P → R and R → Q ), and similarly it also implies that Q → R and R → PThe Truth Table for the compound proposition (p ∨ ¬ q) → (p ∧ q) p q ¬ q (p ∨ ¬ q) (p ∧ q) (p ∨ ¬ q) → (p ∧ q) T T F T T T T F T T F F F T F F F T F F T T F F Equivalent Propositions Two propositions are e quivalent if they always have the same truth value Example Show using a truth table that the conditional is
An entire truth table Replace T ∧T with T Conjunction is true when both parts are true F ∨ T Replace ~T with F and ~F with T Negation gives the opposite truth value T Replace F ∨T with T Disjunction is true when at least one part is true We conclude that the given statement is true' 05Œ09, N Van Cleave 19Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Show that p → q ≡ (∼ p) ∨ q , by using truth table




Chapter 2 The Logic Of Compound Statements Flashcards Quizlet




Long Assignment 1 1 Given Individual Propositions P And Q Verify The Following Logical Equivalences By Constructing A Truth Table For Each Part T Course Hero
Negations of t and c ∼t ≡ c ∼c ≡ t The first circuit is equivalent to this (P∧Q) ∨ (P∧~Q) ∨ (~P∧~Q), which I managed to simplify to this P ∨ (~P∧~Q) The other circuit is simply this P ∨ ~Q I can see their equivalence clearly with a truth table But the book is asking me to show it using the equivalence laws in the Prove without using truth table that $(p↔q)∧(q↔r)∧(r↔p) ≡ (p→q)∧(q→r)∧(r→p)$ I tried to prove this by rewriting the first part using $∧$, $∨$ and the fact that $(p↔q)≡(p→q)∧(q→p)$ to concludeUsing the truth table, verify p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r) Maharashtra State Board HSC Commerce 12th Board Exam Question Papers 195 Textbook Solutions Online Tests 99 Important Solutions 2470 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos & Videos 270



Q Tbn And9gcsh52jlxxs8l9a02kdvxiam8sgn9nognu3yxksi2goutylxc0bm Usqp Cau




Logical Equivalences
View Test Prep quiz1 from CMPE 16 at University of California, Santa Cruz CMPE 16 Spring 14 QUIZ 1 Name ! (i) Truth table for p ↔ q (ii) Truth table for ((¬ p) ∨ q) ∧ ((¬ q) ∨ p) The last columns of statements (i) and (ii) are identical So, p ↔ q ≡ ((¬ p) ∨ q) ∧ ((¬ q) ∨ p)Using the truth table, prove the following logical equivalence p ↔ q ≡ (p ∧ q) ∨ (~p ∧ ~q) Mathematics and Statistics



Q Tbn And9gctl2zcptshv3iyzy8meoqsjchgvcibdk4dy7nnneafmqmi2cwbv Usqp Cau
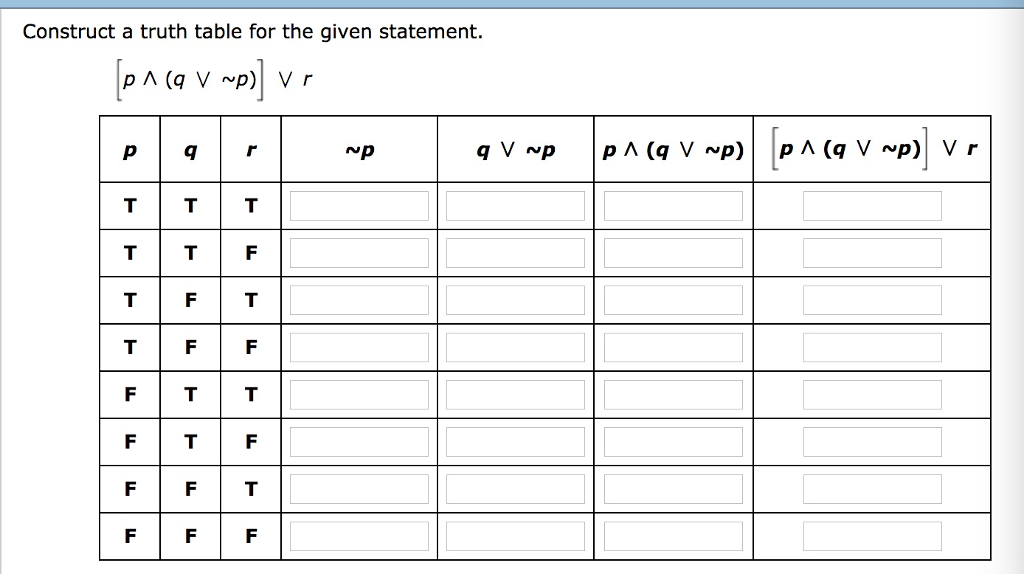



Solved Construct A Truth Table For The Given Statement P Chegg Com
(~p ∧ q) ∨ ~r true Write a negation for the statement Some athletes are musicians everyone is asleep all athletes are not musicians When using a truth table, the statement q → p is equivalent to ~q ∨ p true Decide whether the statement is true or false If q is false then the statement (p ∧ q) → p must be trueStochastic Truth Table A stochastic truth table is a truth table where each row is assigned a number between 0 and 1, and the sum of these numbers is 1 That is, if the stochastic truth table has n n n rows, where each row i i i is assigned the number p i p_i piView Homework Help hw1solns from CMPE 16 at University of California, Santa Cruz HW 1 Solutions CMPE 16 Summer 16, Professor Tantalo Sam Mansfield 11 Problem 14 ad a r q b pqr c rp d p q




Truth Table For Compound Statements Youtube




Construct A Truth Table For P Q P Q Q Brainly In
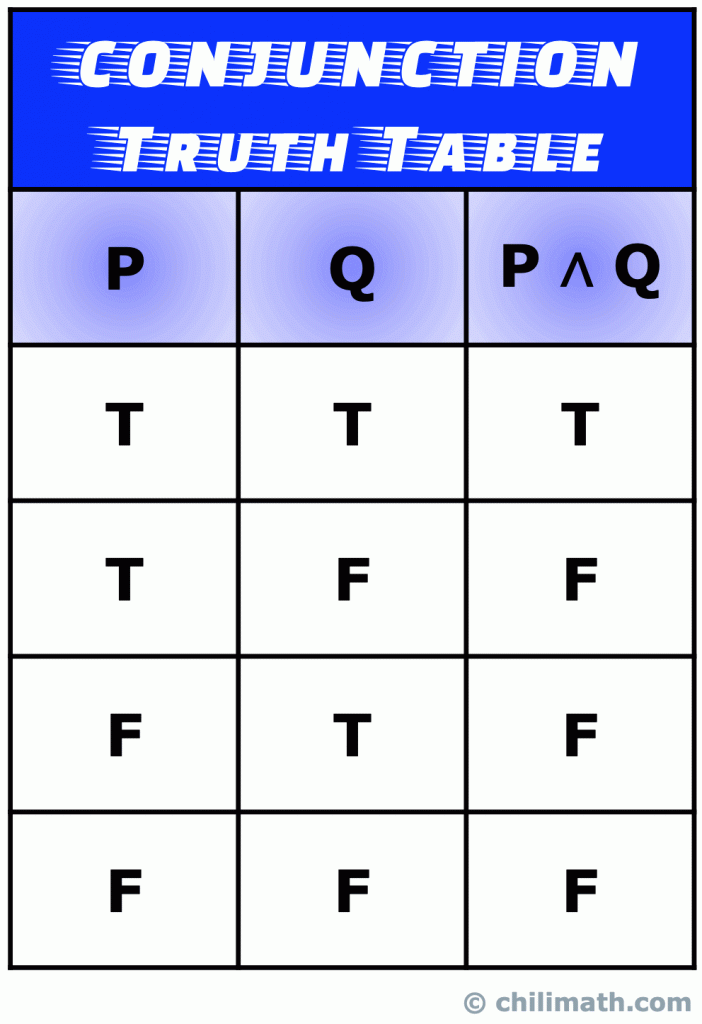
If p p p and q q q are two simple statements, then p ∧ q p \wedge q p ∧ q denotes the conjunction of p p p and q q q and it is read as "p p p and q q q" _\square The truth table for the conjunction p ∧ q p \wedge q p ∧ q of two simple statements p p p and q q q The statement p ∧ q p \wedge q p ∧ q has the truth value T whenever7 According to one of DeMorgan's Laws, ∼ (p∨q) is logically equivalent to (∼ p)∧(∼ q) Use truth tables to prove that these two statements are logically equivalent Then, explain in your own words why the fact that these two statements are equivalent makes sense p q p∨q ∼ (p∨q) T T T F T F T F F T T F F F F T p q ∼ p ∼ qMaking a truth table Let's construct a truth table for p v ~q This is read as "p or not q" Step 1 Make a table with different possibilities for p and q There are 4 different possibilities Case 4 F F Case 3 F T Case 2 T F Case 1 T T p q



Answer In Discrete Mathematics For Ahmed 994



Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
Where, p and q are the inputs, ∧ is the AND operator and ∨ is the OR operator New questions in Mathematics The function h(x) = x2 14x 41 represents a parabolaP Q (P v Q) (P v Q) ==> P T T T T T F T T F T T F F F F T So this is NOT a tautology If P is False and Q is True that does NOT imply that P is True~(p ∨ q) asked in Mathematics by sekhon_jasdeep finiteanddiscretemath



Solved Use A Truth Table To Determine Whether The Argument Is Valid Or Invalid Course Hero




Prepare The Truth Tables For The Following Mathrm In Sim P Leftrightarrow Q Mathrm Ii P Rightarrow P Vee Q
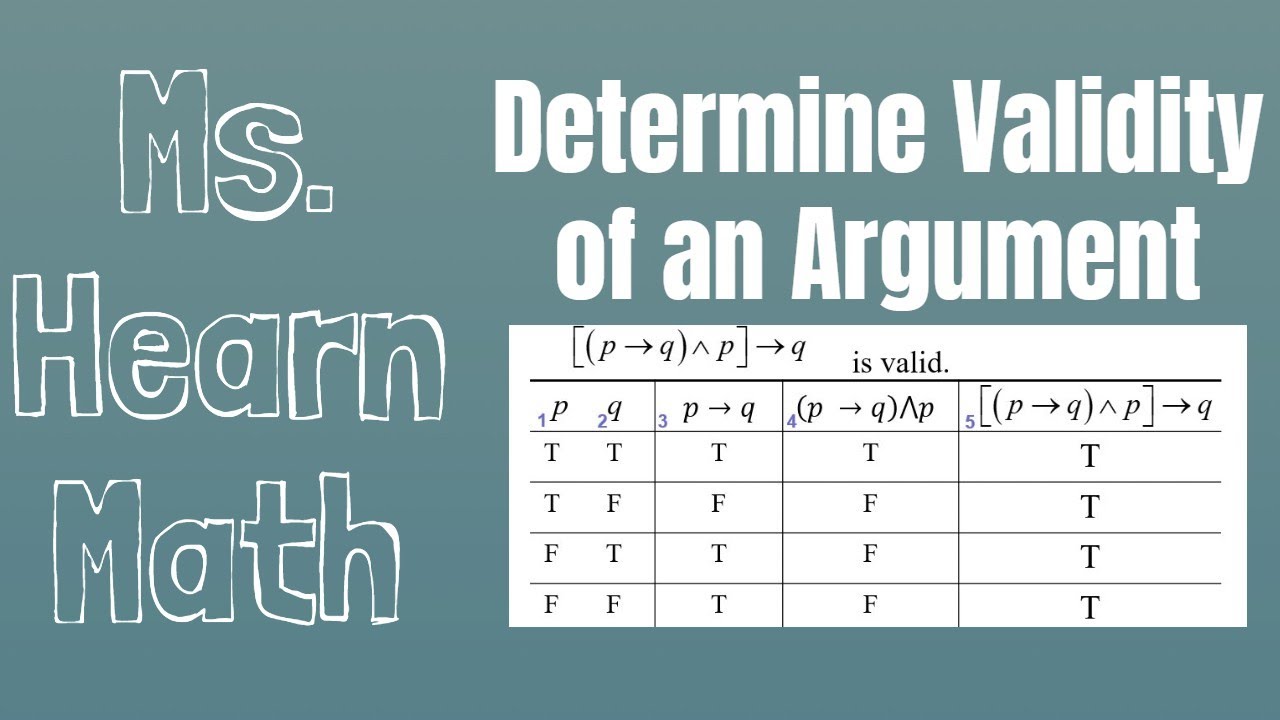
(e) (P ∧ Q)∨(∼P ∧Q)∨(P ∧ ∼Q) is equal to P ∨(Q∧∼P) 9 To show that the circuit corresponding to the Boolean expression (P ∧Q)∨(∼P ∧Q)∨Compound propositions with implication and its truth table in discrete mathematics in hindi,how to make truth table of compound proposition (p∨¬q)→(p∧q),compSec 36 Analyzing Arguments with Truth Tables Some arguments are more easily analyzed to determine if they are valid or invalid using Truth Tables instead of Euler Diagrams Thus, the argument converts to ((p∨q) ∧ ∼ p) → q p q ((p∨q) ∧ ∼ p) → q T T T F F T F F Do I have the flu?




Complete The Following Truth Table By Filling In The Chegg Com



Truth Tables Of Compound Propositions
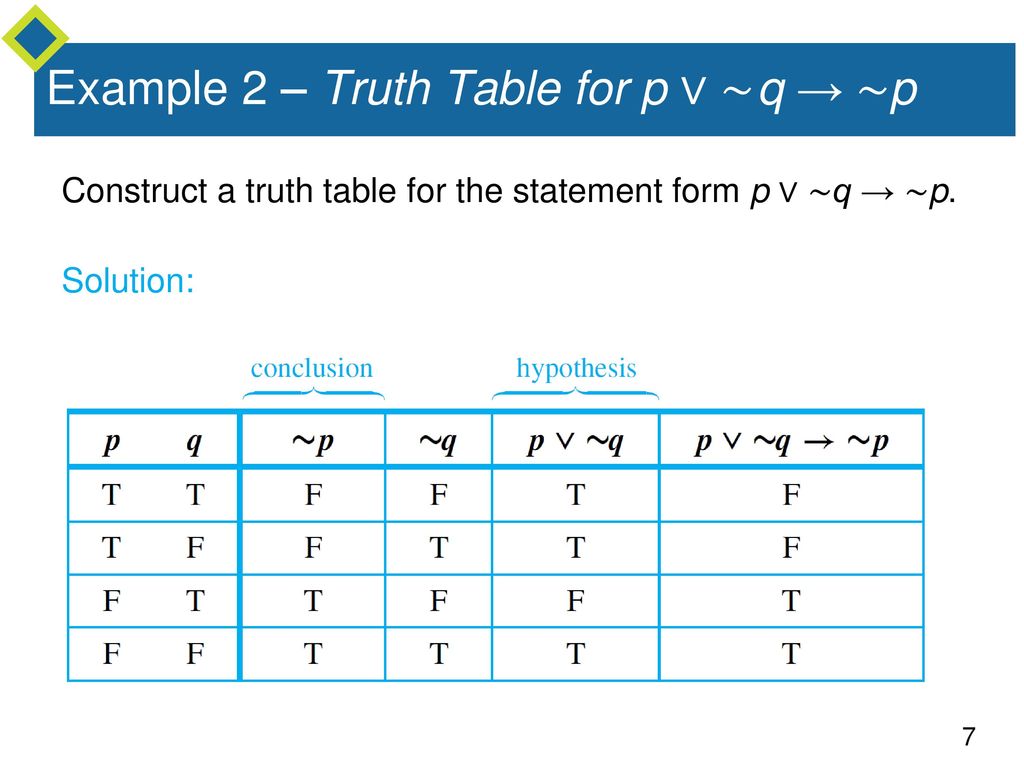
Then since P → Q, we have Q, and therefore ¬ P ∨ Q is true if P is true Now instead, suppose ¬ P Then clearly ¬ P ∨ Q Whether P is true or false, we have ¬ P ∨ Q, so we've shown that P → Q implies ¬ P ∨ Q Conversely, suppose we know ¬ P ∨ Q To prove that P → Q, we assume P and prove Q Assuming P, ¬ P must be false, so ¬ P ∨ 2 The truth table for (p ∨ q) ∨ (p ∧ r) is the same as the truth table for A p ∨ q B (p ∨ q) ∧ r C (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∧ r) D (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)Truth Table Generator This tool generates truth tables for propositional logic formulas You can enter logical operators in several different formats For example, the propositional formula p ∧ q → ¬r could be written as p /\ q > ~r, as p and q => not r, or as p && q > !r




Logic Truth Table For P Q R Q Youtube



Www Uplifteducation Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 291 Logic Practice 2 Key Pdf
Recall that P ∨ ¬ Q is the same as Q → P So the formula of the question is equivalent to (Q → P) ∧ (R → Q) ∧ (P → R)Once the table is there, use the button "Show intermediate results" or "Hide intermediate results" to show or hide intermediate results in the table Since 21 you may enter more than one proposition at a time, separating them with commas (eg " P∧Q, P∨Q, P→Q")If P is false and Q is false, then P → (Q ∧ ¬ P) is true, because ¬ P ∨ (Q ∧ ¬ P) is true as above, since P is false, by the valuation rule for negation ¬ P is true, so the disjunction as a whole is true, because the former disjunct is true Notice what the material conditional is not saying it's not saying the consequent is true Nor is it saying that the antecedent makes the consequent true




Part 1 Math170 E Portfolio




Use A Truth Table To Determine Whether The Following Statement Is A Contradiction A Tautology Or Brainly Com
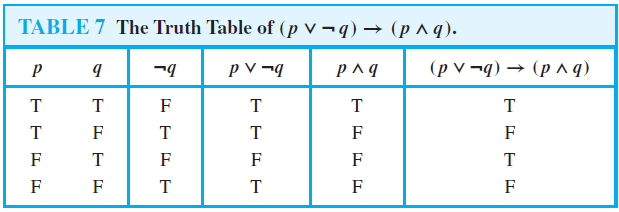
I am having a little trouble understanding proofs without truth tables particularly when it comes to → Here is a problem I am confused with Show that (p ∧ q) → (p ∨ qThe truth table for p AND q For two propositions, XOR can also be written as (p ∧ ¬q) ∨ (¬p ∧ q) Logical NAND The logical NAND is an operation on two logical values, typically the values of two propositions, that produces a value of false if both of its operands are true(p ∨¬q) → (p ∧ q) Solution Because this truth table involves two propositional variables p and q, there are four rows in this truth table, one for each of the pairs of truth values TT, TF, FT, and FF The first two columns are used for the truth values of p and q, respectively



Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences



Truth Tables Of Five Common Logical Connectives Or Operators Chilimath
Propositional Logic, Truth Tables, and Predicate Logic (Rosen, Sections 11, 12, 13) TOPICS • Propositional Logic • Logical OperationsIn this case, the truth values for ~(p∧q) and ~p∨~q are exactly the same, so we can conclude that the two statements are equivalent ~(p∧q)≡~p∨~qSo, if we ever encounter ~(p∧q), we can replace it with ~p∨~q without changing the logical meaning of the statement!1 (10 points) State (true or false) which of the following expressions are




Chapter 10 Truth Tables



Uomustansiriyah Edu Iq Media Lectures 6 6 17 02 08 01 11 58 Am Pdf
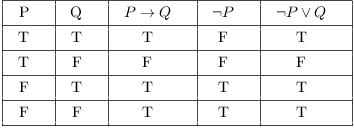
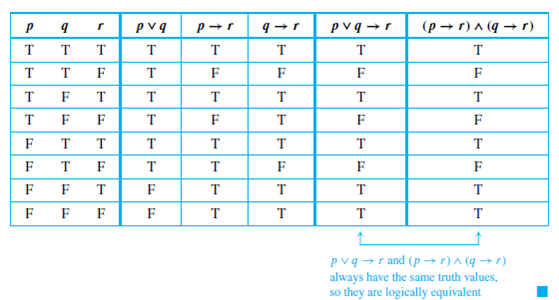
T In the above truth table, the entries in columns 3 and 7 are identical ∴ ~ (p ∨ q) ∨ (~ p ∧ q) ≡ ~ p Concept Mathematical Logic Statement Patterns and Logical Equivalence Report ErrorThe truth table for ((p∨(r∨q))∧∼(∼q∧∼r) is the same as the truth table for Question options (p∨q)∧∼(p∨r) (p∧q)∨(p∧r) ((p∨r)∨q))∧(p∨r) (p∧r)∨(p∧q) q∨r Expert Answer Who are the experts?11 PROPOSITIONS 7 p q ¬p p∧q p∨q p⊕q p → q p ↔ q T T F T T F T T T F F F T T F F F T T F T T T F F F T F F F T T Note that ∨ represents a nonexclusive or, ie, p∨ q is true when any of p, q is true and also when both are true On the other hand ⊕ represents an exclusive or, ie, p⊕ q is true only when exactly one of p and q is true 112



1



Truth Table For Any Proposition Tautologies Logical Equivalence Contradiction 13 Youtube
Now let's try comparing two more complex statements to see if they are equivalent(p ∧q)∧ ~ (p ∨ q) is a contradiction (ie is always false) Set up a truth table with a column for each temporary proposition that you need as was done in the previous problem 5 44 Show that the propositions ~ (p ∧ q) and ~ p∨~ q are logically equivalent Note This is one of DeMorgan's laws 6 45 Use the laws in Table 41 to show that ~ (p ∨q)∨(~ p ∧ q)Explain, without using a truth table, why (p ∨¬q) ∧ (q ∨¬r) ∧ (r ∨¬p) is true when p, q, and r have the same truth value and it is false otherwise ?




Construct A Truth Table For The Following Statement Form P Q R P N Q R Brainly In




Truth Table
View cs22_hw6pdf from CS 22 at University of Texas Homework 6 CS22 Homework HW 6 1 Homework 6 Problem 61 a CNF ¬p ∨ ¬q p 1 1 0 1 q (p ∧ ¬q) ∨ ¬p ¬pShare It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 2 votes answered by Abha01 (515k points) selected by RupaBharti Best answer Truth Table41) (a) Draw a tree for the statement ~ (p∧q)∨(~p∧r) (b) Assuming p has truth value T, q has truth value T, and r has truth value F, use the tree to find the truth value of the statement form Let p be the TRUE statement "The sun is a star" and q be the TRUE statement "The moon is a planet" Determine the truth value of the given statement




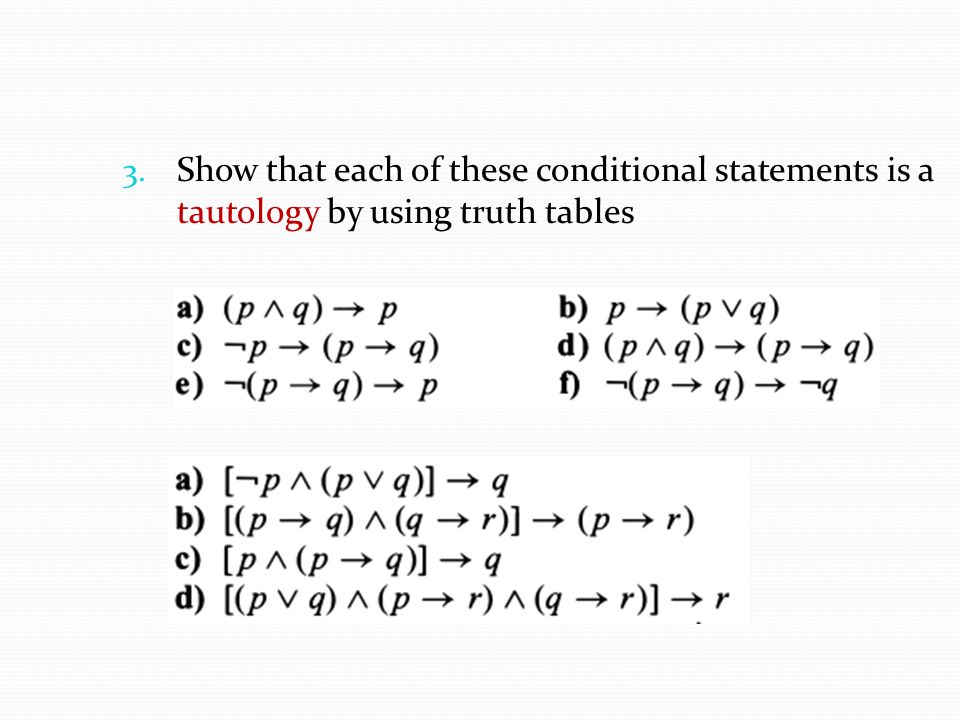
Show That Each Conditional Statement Is A Tautology Without Using Truth Tables A Neg Pwedge Pv Q To Q B P To Q Wedge Qto R To Pto R C Pwedge Pto Q To Q D




Proving Neg R To P Lor Neg Q To Neg P Land R To Q To Neg P Lor Q Is A Tautology Without A Truth Table Mathematics Stack Exchange
Verify the following proposition with the help of a truth table (P∧Q)∨(P∧~Q) = P icse;0 Describe how to negate an existentially quantified statementWithout using truth table prove that (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ ∼ q) ≡ p Maharashtra State Board HSC Arts 12th Board Exam Question Papers 167 Textbook Solutions Online Tests 70 Important Solutions 1872 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos & Videos 321



Answer In Discrete Mathematics For Angelica Aguilar




Show That P Q Q R Is Equivalent To P R P Q R Q Mathematics Stack Exchange
3 rows (p ∨ Q) ∧ (p ∨ ~q) P Q ~p ~q (p∨q) (p∨~q) (p∨q)∧(p∨~q) T T T F F(For this problem, we cannot only use p and q to determine if the proposition is satisfiable since we would have p V q and the negated value meaning p or q is needed to be false to get both true However, since we also had ~p V q and ~q V p it would result in a false value in all scenarios Thus, r was added into the table which allows us to get a satisfiable composition proposition valueThe truth table for (P ∨ Q) ∧ (P ∨ ~Q) ∨ P What is T T F F 0 Let A = {2,4,6,8,10} and B = {4,8,10} The difference between A and B (Find A B) What is A B = {2,6}?
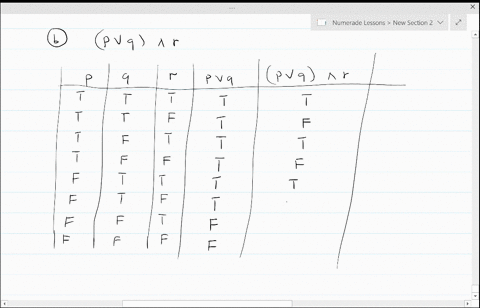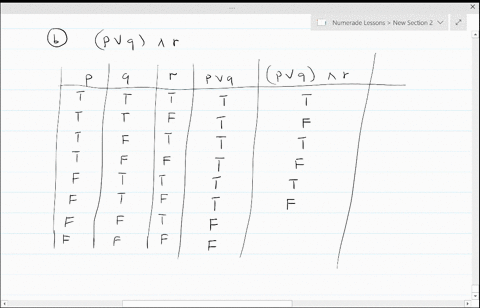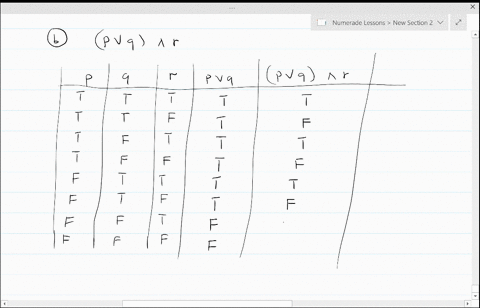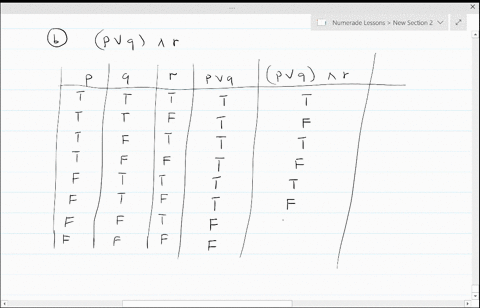



Solved Construct A Truth Table For Each Of These
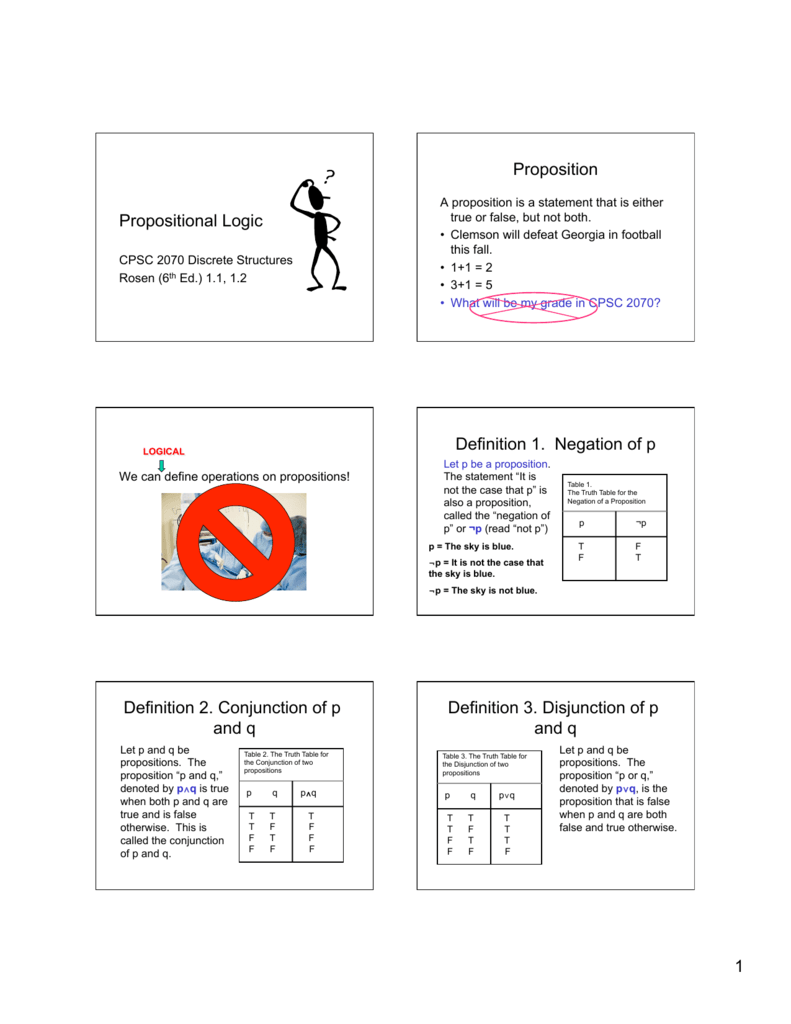



1 Propositional Logic Proposition Definition 1 Negation Of P




Logic And Proofs



Logic Truth Table For P Q R Q Youtube



Www Cs Unc Edu Yangk Comp2 Homework Hw1 Solution Pdf




Dm T




What Is The Truth Table For P Q Q R P R Quora




Conditional Statements Let P And Q Be Statements




Construct The Truth Table For The Compound Chegg Com



Propositional Logic Truth Table Boolean Algebra Dyclassroom Have Fun Learning



Logic And Set Notation



Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 02 Youtube



Conditional Statements Ppt Download



Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalence




Prove That Neg P Wedge Q Leftrightarrow Neg P Vee Neg Q Using Truth Table Mathematics Stack Exchange




Using A Truth Table To Prove Or Disprove P Vee Q Wedge R P Wedge Q Vee R And P Wedge Q Vee R P Vee Q Vee R Mathematics Stack Exchange




Construct The Truth Table For P Q R
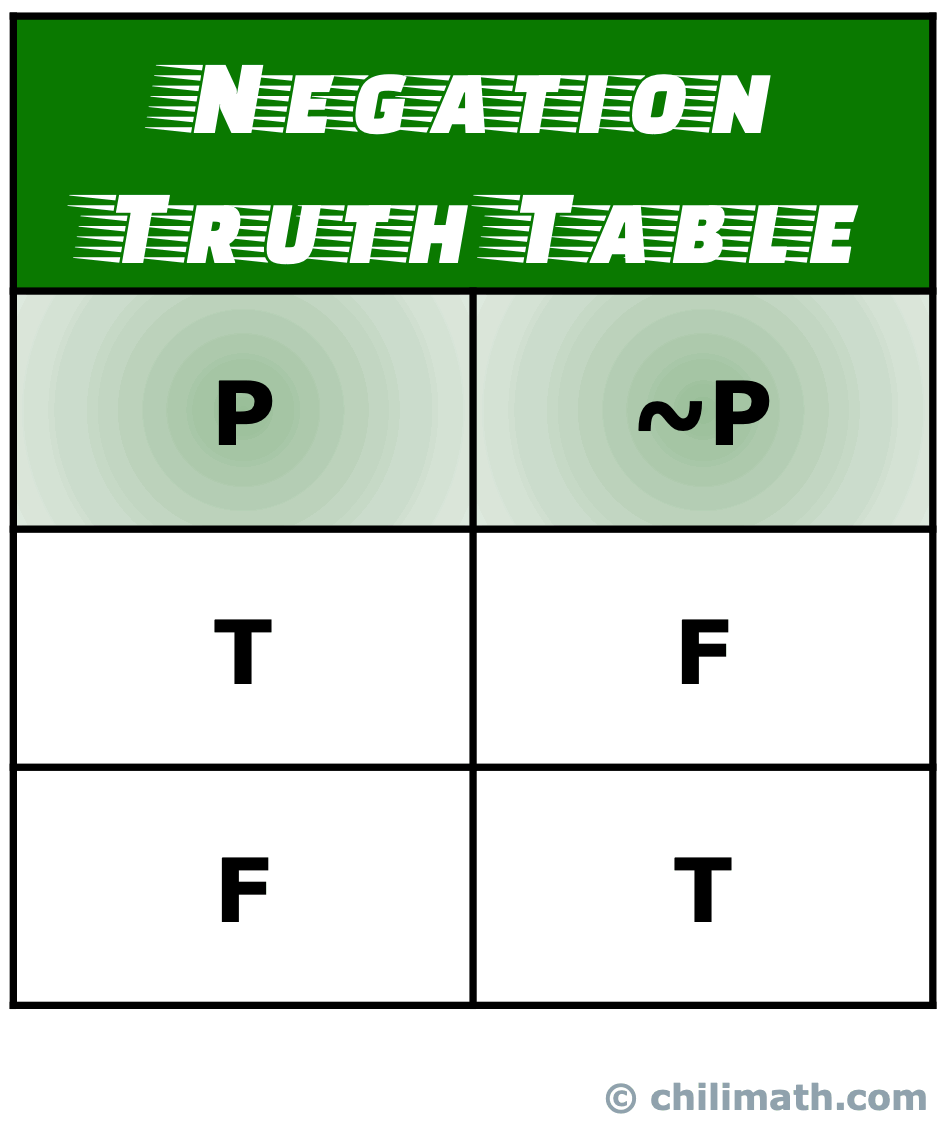



Truth Tables Of Five Common Logical Connectives Or Operators Chilimath




Show That P Q Q R P R Is A Tautology By Using The Rules
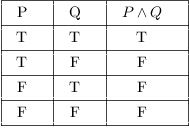



Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences



Prove That P Q R P Q R Using Truth Table Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
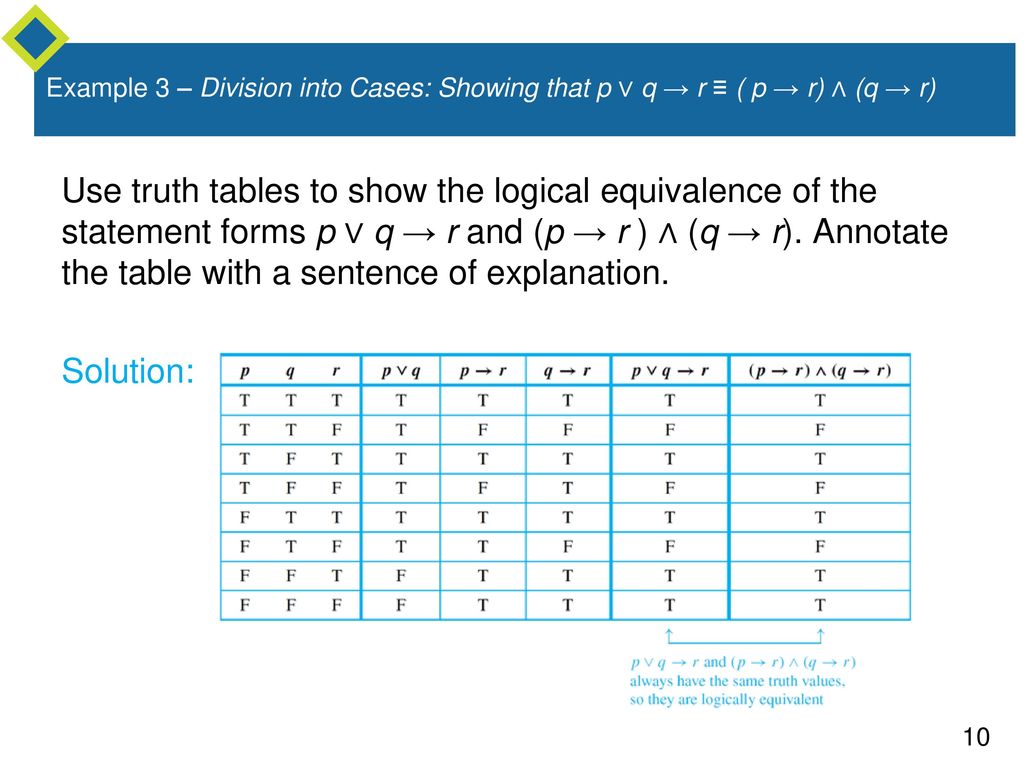



Conditional Statements Ppt Download




Chapter 10 Truth Tables




Prepare The Truth Table Of The Following Statement Patterns I P To Q Wedge Q To P Ii P Wedge Q To Sim P Iii P




Using Truth Table Prove The Following Logical Equivalence P Q Rarr R P Rarr Q Rarr R Youtube




10 Prepare The Truth Tables For The Following Paq Iii P A V Q P



Storm Cis Fordham Edu Zhang Cs2100 Slides Logic Pdf




Chapter 2 The Logic Of Compound Statements Flashcards Quizlet



2 Circuits And Truth Tables Sireum Logika



Answer In Discrete Mathematics For Javairia 1236
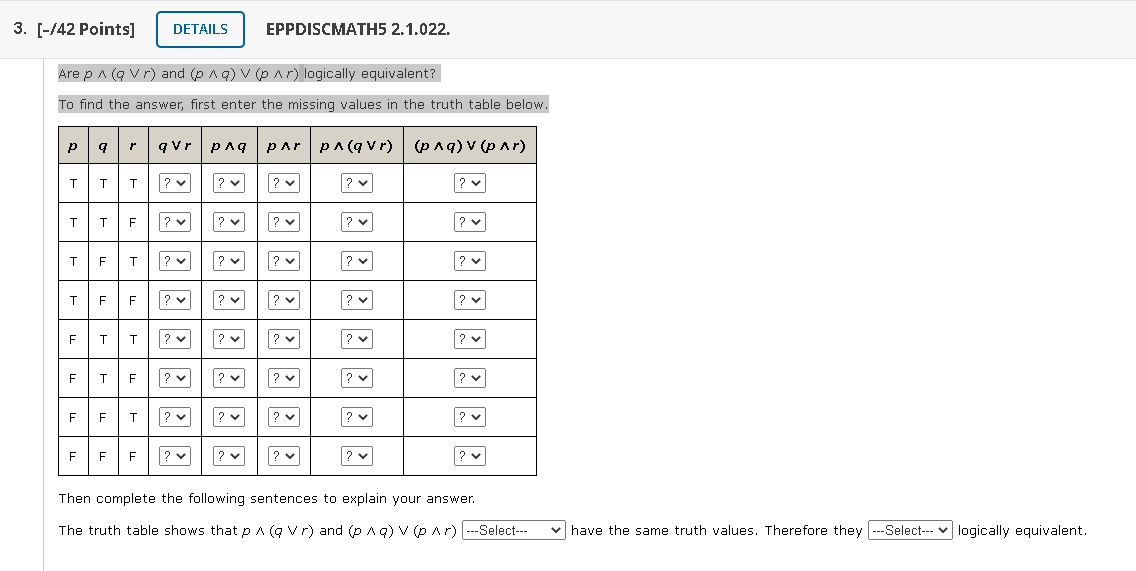



Are P Q R And P Q P R Logically Chegg Com




Analyzing Compound Propositions With Truth Tables Mathbootcamps




Truth Tables Brilliant Math Science Wiki




Analyzing Compound Propositions With Truth Tables Mathbootcamps
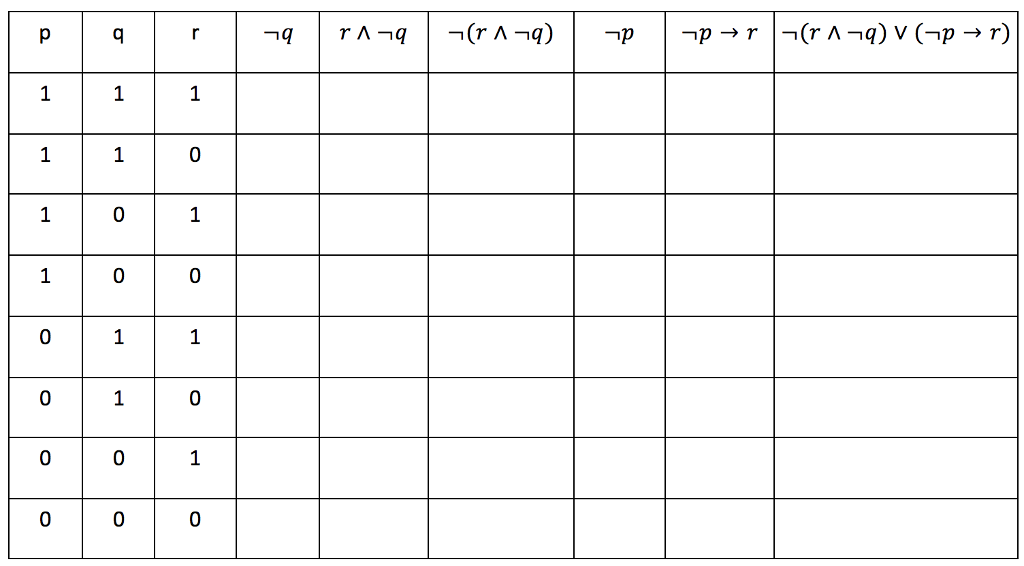



Write A Truth Table For The Proposition Chegg Com




Analyzing Compound Propositions With Truth Tables Mathbootcamps



Answer In Discrete Mathematics For Sushii



Http Kennethsokc Weebly Com Uploads 3 9 8 0 Practice Logic Pdf



How To Compute For The Truth Table Of F G F G How Do You Use The Truth Tables Method To Determine Whether P Q Q And P Are Logically
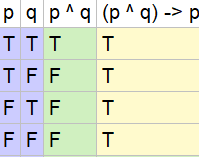



Show That Each Of These Conditional Statements Is A Tautology By Using Truth Tables A P Q P B P P Q C P P Q
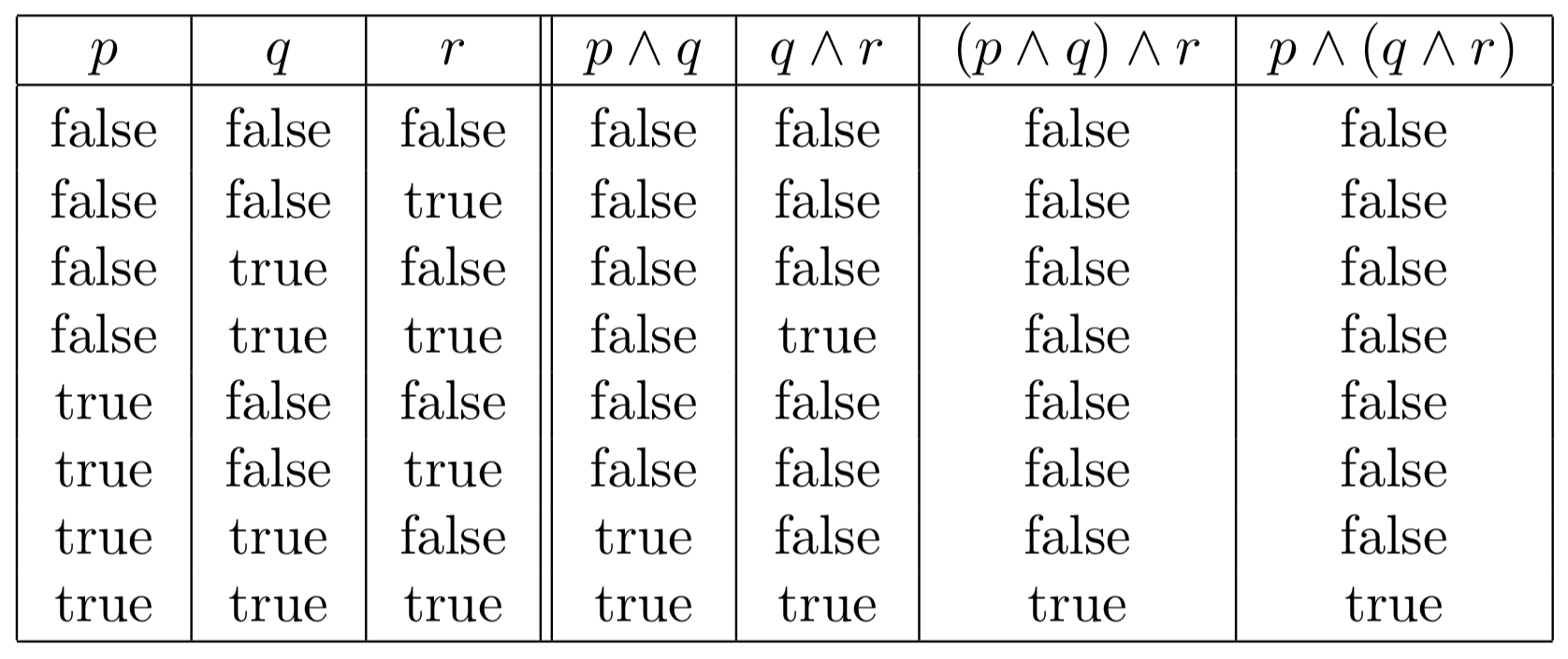



1 1 Propositional Logic Engineering Libretexts



Propositional Logic Truth Table Boolean Algebra Dyclassroom Have Fun Learning




Solved Construct A Truth Table For Each Of These




Analyzing Compound Propositions With Truth Tables Mathbootcamps
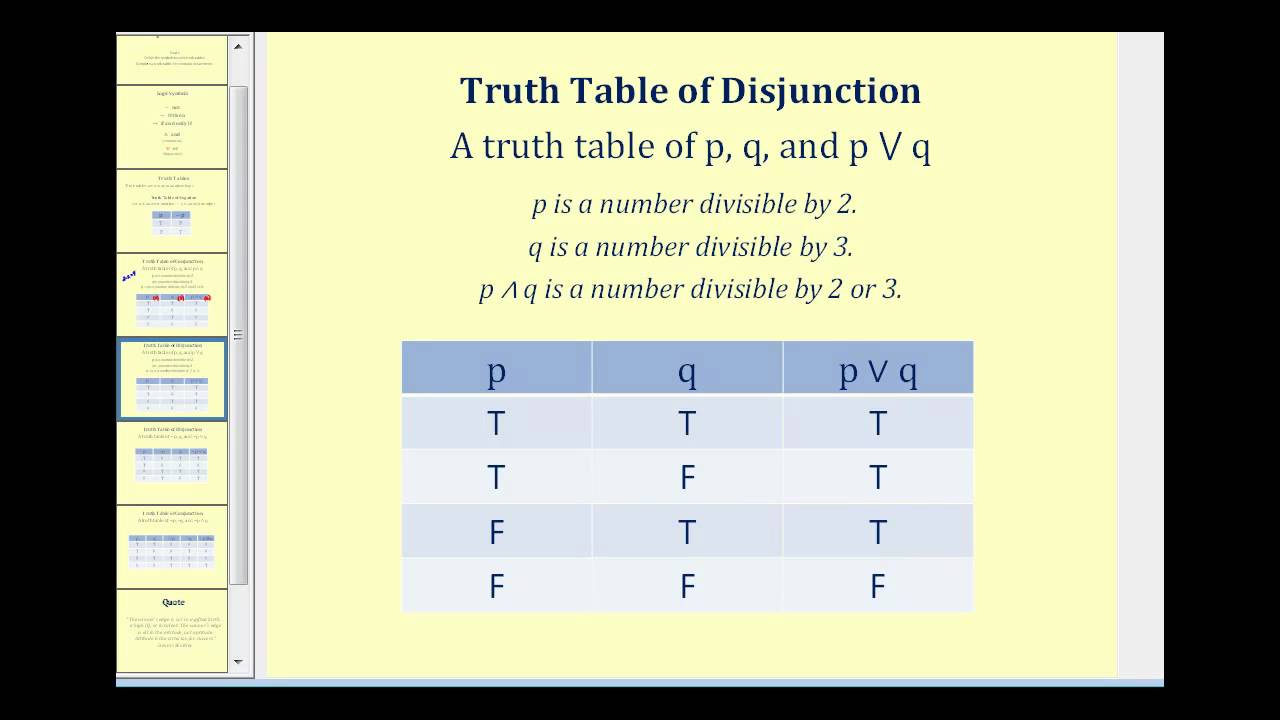



2 8 Truth Tables K12 Libretexts




Part 1 Math170 E Portfolio




Logic And Proofs



Solved Use The Logical Equivalence Established In Example To Rew Chegg Com



Exercises On Propositional Logic Due Tuesday Septem Flip Ebook Pages 1 5 Anyflip Anyflip



Condor Depaul Edu Ntomuro Courses 400 Bookslides Eppdm4 02 02 Pdf



P Q R Q R Q R Q P Par Chegg Com




Using A Truth Table To Prove Or Disprove P Vee Q Wedge R P Wedge Q Vee R And P Wedge Q Vee R P Vee Q Vee R Mathematics Stack Exchange



Www Site Uottawa Ca Lucia Courses 2101 10 Lecturenotes 02propositionallogic Pdf



Show That P Q Q R P R Is A Tautology By Using The Rules



Www Site Uottawa Ca Lucia Courses 2101 10 Lecturenotes 02propositionallogic Pdf




The Truth Table Represents Statements P Q And R Which Statement Is True For Rows A C And E R Brainly Com




Show That Each Conditional Statement Is A Tautology Without Using Truth Tables A Neg Pwedge Pv Q To Q B P To Q Wedge Qto R To Pto R C Pwedge Pto Q To Q D



Solved Construct A Truth Table For Each Of These
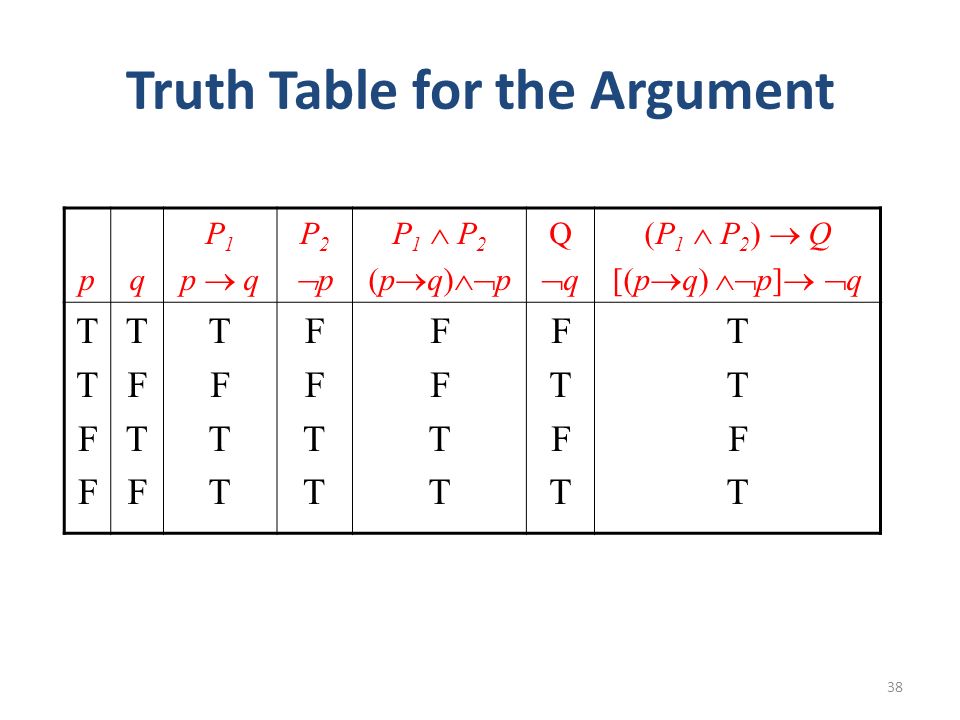



Reading Chapter 4 44 59 From The Text Book Ppt Video Online Download




How Do I Find The Truth Value In This Logic Problem P Lor S Land Neg Q Rightarrow R Rightarrow S Mathematics Stack Exchange



Http Eng Usf Edu Hady Courses Mgf1106 Documents Slides 3 3 Pdf



How To Construct The Truth Table Of P Q Quora




Logic Part 3 Truth Tables Ethical Realism
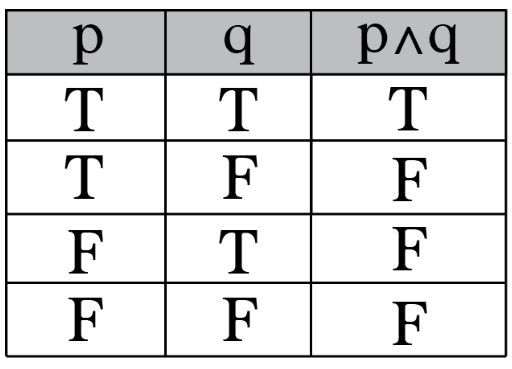



I Need Help With If P P Q Is False Then The Truth Values Of P And Q Are Respectively



Www Usna Edu Users Cs Roche Courses F19sm242 Get Php F Slides2 1b Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcr2oxnmnlu9pdclqvbtg6glfskyfgzj1 Hn4uchqb7nttyoluij Usqp Cau




Proving Each Conditional Statement Is A Tautology Mathematics Stack Exchange
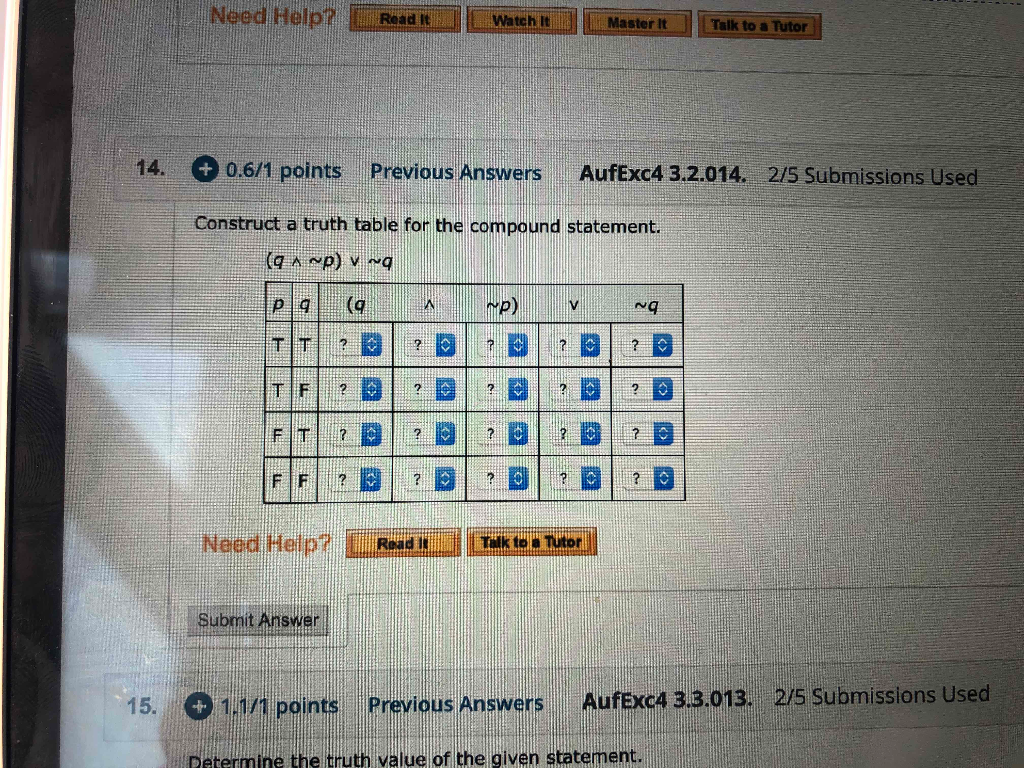



Solved Construct A Truth Table For The Compound Statement Chegg Com




Truth Table Free Math Worksheets




Construct The Truth Tables For The Following Expressions A P Q R B P Q P R C P Brainly Com




Without Using Truth Table Prove That Pvvq P Toq Is A Tautology Youtube
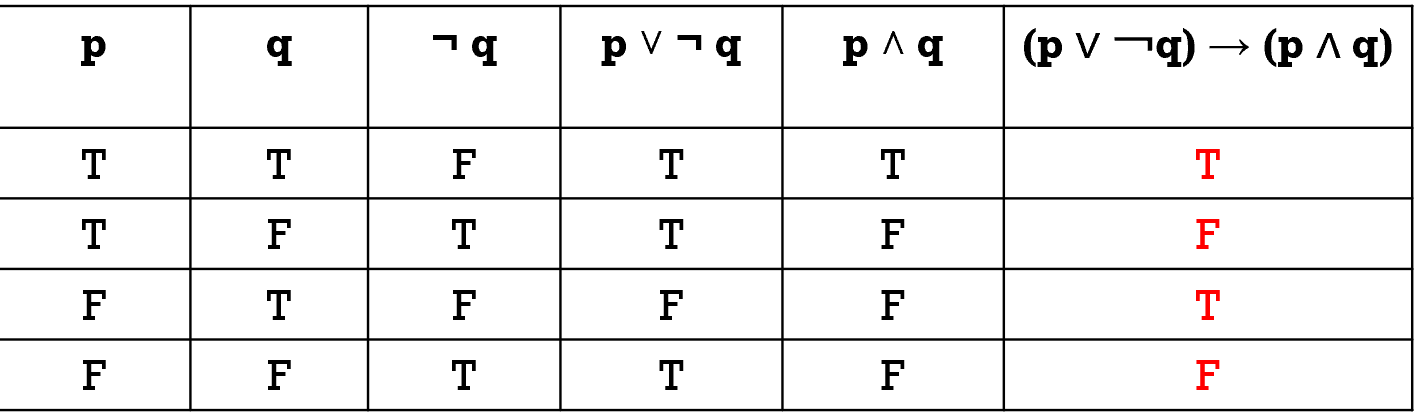



Introduction Truth Tables
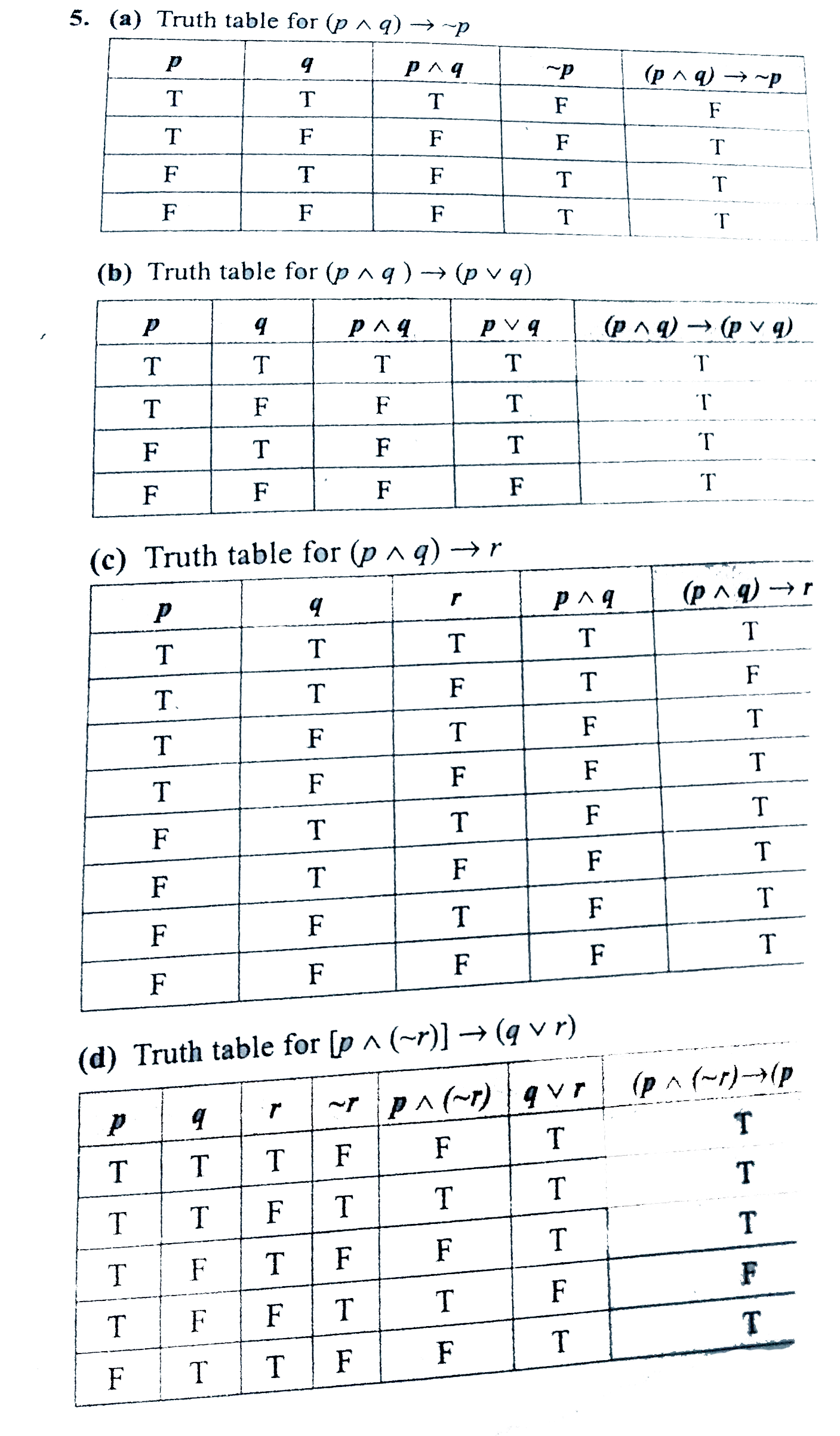



Construct The Truth Table For The Followings Statements Br



Answer In Discrete Mathematics For Angelica Aguilar



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿